Symptoms such as loss of sensation, loss of movement, temporary or permanent visual impairment, fainting are among the symptoms of many health problems. However, it must be noted that carotid artery occlusion can also cause these symptoms. Stating that unnoticed vascular occlusions can cause severe conditions like stroke or paralysis, Liv Hospital Vascular Surgery Specialist Prof. Dr. Erdal Aslim explained the treatment of carotid artery disease.
How does it occur?
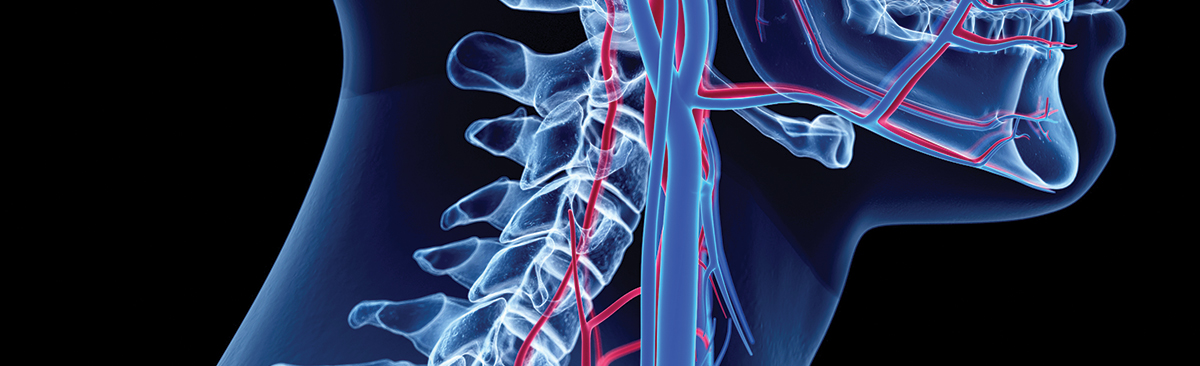
Carotid artery disease is one of the main causes of stroke, along with heart problems and brain hemorrhages. The disease occurs as a result of narrowing or occlusion of the carotid arteries, which goes along the both sides of the neck into the skull and are responsible for blood supply of two hemispheres of the brain.
What are the causes?
- Tobacco use
- High level of fat and cholesterol in the blood
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar due to insulin resistance or diabetes
- Genetic factors
- Diabetes
What are the symptoms?
Loss of strength and movement in arm and/or leg at the opposite side of the affected carotid artery, permanent or temporary vision loss on the affected side, blackout, unconsciousness, facial paralysis and speech disorders.
Can cause paralysis
When the occluded carotid arteries become unable to supply the blood necessary for the brain, it can cause complaints like forgetfulness, dizziness, short-term speech or visual impairment, blackout. Patients may faint in case of more severe occlusions. The most troublesome outcome of this disease is the stroke possibility. Reduced blood circulation may leave certain areas of the brain without blood supply. If the blood clots accumulating in the occluded carotid artery travels to the brain, they can cause sudden death or permanent major paralysis.
How it is
Lifestyle-nutrition changes: Maintaining a healthy diet and optimal weight is helpful for maintaining the cholesterol levels within the normal range and preventing the development of high blood pressure. Such precautions can prevent the disease and/or its progression.
Medical treatment: Accompanying diseases are treated with risk management; blood thinners and vasodilators are administered.
Interventional treatment: This treatment is performed for carotid arteries that are narrowed but not totally occluded. No interventional treatment is required for occluded carotid artery.
Surgical treatment: If the occluding plaque is required to be removed by endarterectomy method under general, regional or local anesthesia, the surgical treatment includes the expansion of the narrowed carotid artery by using synthetic or autologous patches, or the direct closure if the diameter is sufficient.
Interventional radiological treatment: Stent method is being used for the occlusion of neck vessels. This method is only applicable for a select patient group or in cases where operation cannot be performed for other reasons because short-term results published for this method do not present any advantage over surgery and no long-term results have been obtained yet.