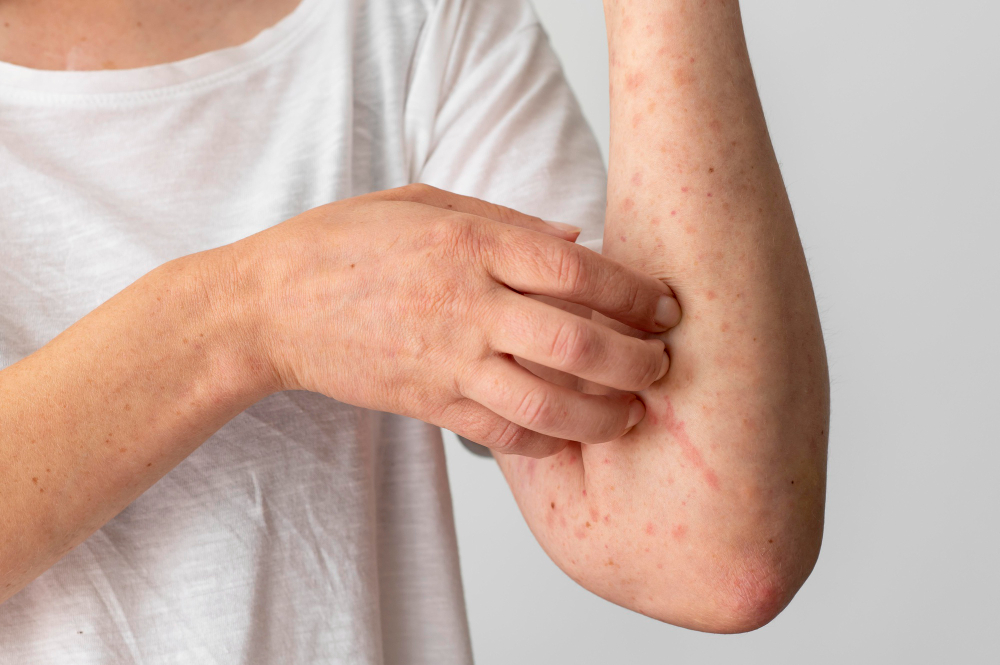
Actinic keratosis, or solar keratosis, may sound rare, but it is more common than you imagine. Actinic keratosis, while not a type of skin cancer in and of itself, is seen as a severe warning sign since if neglected, it has the potential to develop into squamous cell carcinoma. For the early detection and prevention of skin cancer, it is vital to comprehend and recognize AK.
What Is Actinic Keratosis?
A common skin ailment known as actinic keratosis (AK), often called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is characterized by rough, scaly patches or lesions that appear on sun-exposed parts of the skin. It is considered a precancerous condition because, if untreated, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a kind of skin cancer, may develop from it. The ICD 10 code for actinic keratosis is L57 and denotes the condition.
Fair-skinned people, those with light-colored eyes, and people who spend much time outside without sunscreen are more likely to get it. It has a variation known as lichenoid actinic keratosis (LAK). LAK resembles standard AK lesions but exhibits additional lichenoid or inflammatory characteristics. A more prominent inflammatory reaction that resembles lichen planus, a distinct skin condition, may be seen in the affected skin. Almost the same treatment methods are followed for both conditions.
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a typical benign tumor-like development of the skin that is not malignant. Seborrheic keratoses can appear on many different body portions, especially those exposed to the sun. Older persons are more likely to have them. They pose no health risks and are not spreadable. Although seborrheic keratoses are primarily harmless, some people may find them unsightly. Although they don’t need to be treated, removal may be done if they become sensitive or inflamed or for aesthetic reasons. A dermatologist can identify the condition and offer management advice for seborrheic keratosis.
Contact our medical experts in Istanbul to understand the causes of actinic keratosis!

Actinic Keratosis Vs. Basal Cell Carcinoma
Precancerous actinic keratosis is a skin disorder marked by rough, scaly spots from sun exposure. Basal cells in the skin give birth to basal cell carcinoma, a kind of skin cancer. Although they may both have a similar appearance, basal cell carcinoma is more damaging and aggressive, with the potential to spread. Actinic keratosis can develop into cancer. Sometimes these diseases may be misdiagnosed as one another and consulting an expert dermatologist for an accurate assessment and therapy may change the outcomes for these skin conditions.
Learn more about the differences between actinic keratosis and basal cell carcinoma from our medical staff in Istanbul. Book a consultation today!
Actinic Keratosis Symptoms
Actinic keratosis (AK) commonly manifests as rough, dry patches of skin that have been exposed to the sun for a lengthy period. The following list of actinic keratosis symptoms and traits:
- Skin patches: Small, round, oval, flat, or barely elevated skin patches are the most common form of AK. The lesion might be between a few millimeters and a few centimeters.
- Texture: The infected skin may feel like sandpaper or a dry scab, being rough, dry, and scaly.
- Color: Actinic keratosis patches can be skin-toned, pink, red, or brown. They may occasionally be white, yellow, or grayish.
- Location: Sun-exposed parts such as the face (mainly the forehead, nose, and cheeks), ears, lips, neck, scalp, forearms, and backs of hands are where the lesions commonly appear. Areas typically covered by clothing have a lower likelihood of developing them.
- Itching or Sensitivity: A few actinic keratosis spots may itch, burn, or feel pain modestly.
- Peeling and scaliness: The lesions’ surface may start to look dry and scaly; in some cases, the patches may peel or crust over.
Book a consultation with our medical experts in Turkey to get actinic keratosis symptoms checked!
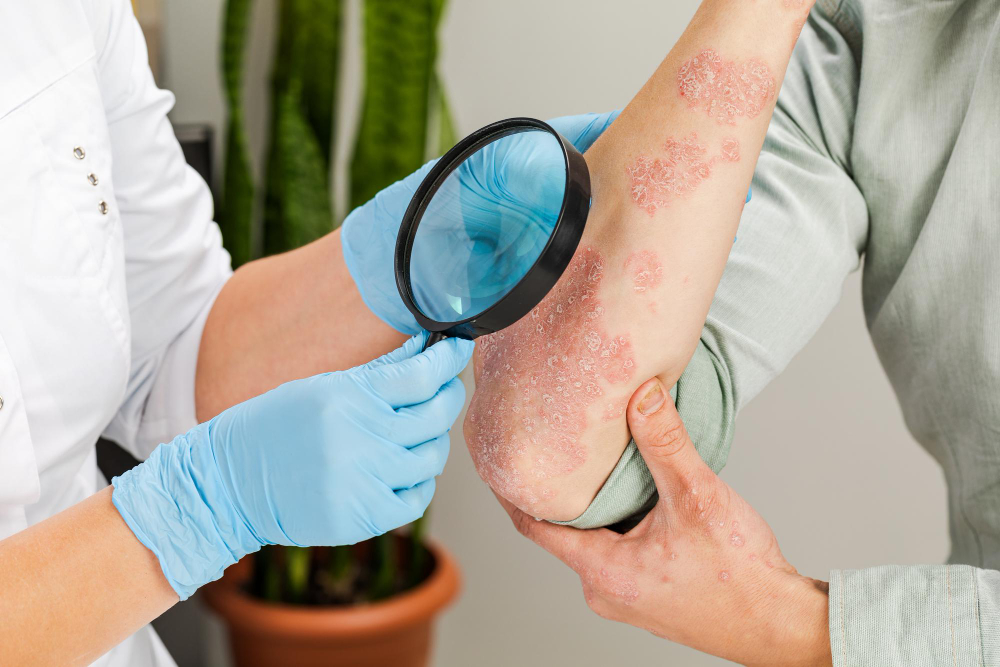
Actinic Keratosis Treatment
Depending on the quantity, size, and location of the lesions as well as the patient’s overall health and medical history, actinic keratosis (AK) can be treated in several ways. The goal of treatment is to get rid of or kill the precancerous cells to lower the risk of developing skin cancer. The following are some typical actinic keratosis treatments:
Cryotherapy:
The afflicted area is treated with liquid nitrogen, freeing and killing the aberrant cells. Eventually, the treated skin may blister and slough off.
Electrodessication And Curettage
After the AK lesion is removed (curettage), an electric current destroys any leftover aberrant cells (electrodesiccation).
PDT: Photodynamic Therapy
The skin is coated with a photosensitizing chemical activated by a particular wavelength of light. AK cells are subsequently destroyed as a result.
Laser Treatment
Laser beams find and eliminate AK cells. When treating more persistent and localized lesions, laser therapy is frequently used.
Peeling Agents
The skin’s outer layer is scrubbed with a chemical solution to remove AK lesions.
Excision Surgery
AKs that are larger or more advanced can require surgical removal. The skin specialist removes the lesion and the surrounding unhealthy tissue.
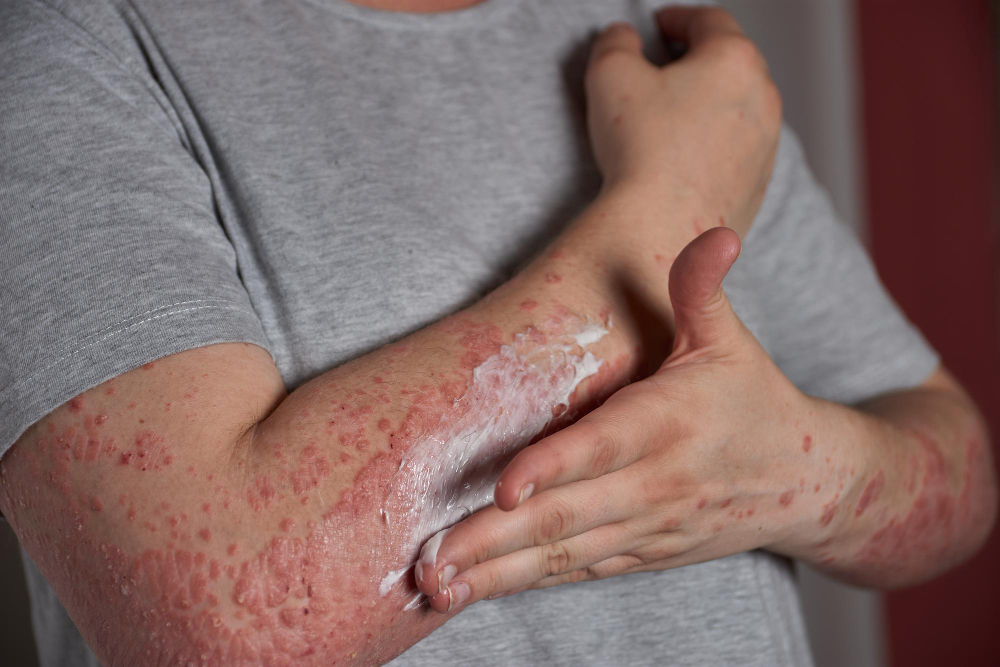
How To Remove Actinic Keratosis At Home?
It is not advised to try to treat actinic keratosis yourself. A dermatologist should adequately diagnose and treat actinic keratosis because it is a precancerous condition. Home cures may not eliminate the lesions; they may also cause complications or postpone getting suitable medical attention. The optimal course of treatment may involve topical drugs, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, or other actions carried out by a healthcare provider. Thus, people should instead seek expert medical guidance. Early detection and treatment can ensure good management of actinic keratosis and halt the progression to skin cancer.
Get actinic keratosis treatment in Istanbul with high-quality medical facilities. Contact us today!
Liv Hospital For Actinic Keratosis Treatments
Liv Hospital in Turkey stands out for people looking for treatment for Actinic Keratosis due to its remarkable international reputation and commitment to healthcare excellence. Liv Hospital, which operates a network of 7 hospitals, exemplifies its brand, “Leading International Vision,” by providing top-notch medical knowledge, state-of-the-art technologies, and a dedication to influencing the course of healthcare. Patients worldwide pick Liv Hospital because it offers top-notch care and cutting-edge methods to treat actinic keratosis. Learn more about actinic keratosis treatment prices in Turkey 2023 by contacting us!